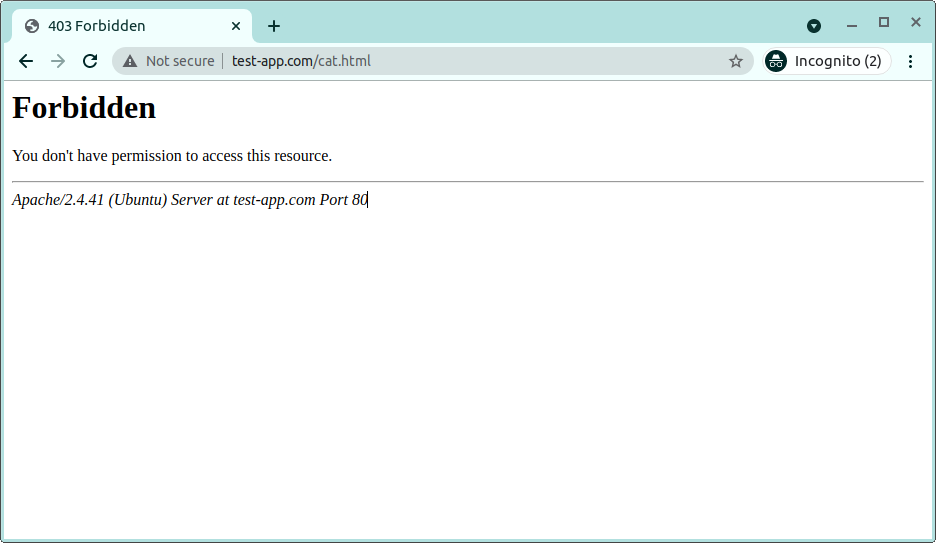
Many web server configurations face issues related to file permissions. It often renders the server inaccessible to visitors and manifests in the form of a 403 error. Usually, the error message is something like "Forbidden: you don't have permission to access / on this server". This error can also restrict access to other routes on the server such as /directory.
Similar issues can also occur due to problems in the Apache configuration file or even because of a corrupt .htaccess file. This guide provides step-by-step solutions to all of these problems. Try them one at a time, starting from the first solution.
What Causes This Apache 403 Error?
This is a fairly common 403 error on Apache's end caused by a myriad of issues. However, in most cases, this error occurs due to the lack of proper permissions needed to access a site publicly. Apart from this, WordPress sites often face this issue due to a bad .htaccess file.
Moreover, since Apache version 2.4, there have been some changes in how directives work. This can also restrict public access to your website and result in a 403 forbidden error.
1. Fix File Permissions to Avoid the Error
Most people face this common 403 error due to the lack of proper permissions. If the site admin forgets to enable read access to the outside world, then end-users will be unable to access the requested resource. This is often the root cause of this error.
If you're a site admin instead, you need to make sure files intended for public access have proper read permissions. Else, if you're facing this error on a public site, inform the site administrator to solve this issue.
Setting the correct permissions for publicly accessible files can be a bit tricky. That's why admins should start with absolutely zero permissions and add them as needed. It's a good idea to have folders with permission mode of 755 and files with 644.
For a simple website, the directories need to have execute permission, and files should have read permission. Make sure not to give execute permission on files. Malicious users can gain unwanted access to public servers via such files. The permission mode for Read, Write and Execute access is 4, 2, and 1, respectively.
So, a permission mode of 755 on directories means only the owner has full access to the directory contents. Group users and others can only read and execute. Similarly, 644 permission mode for files provides read and write access to the owner and only read access to everyone else.
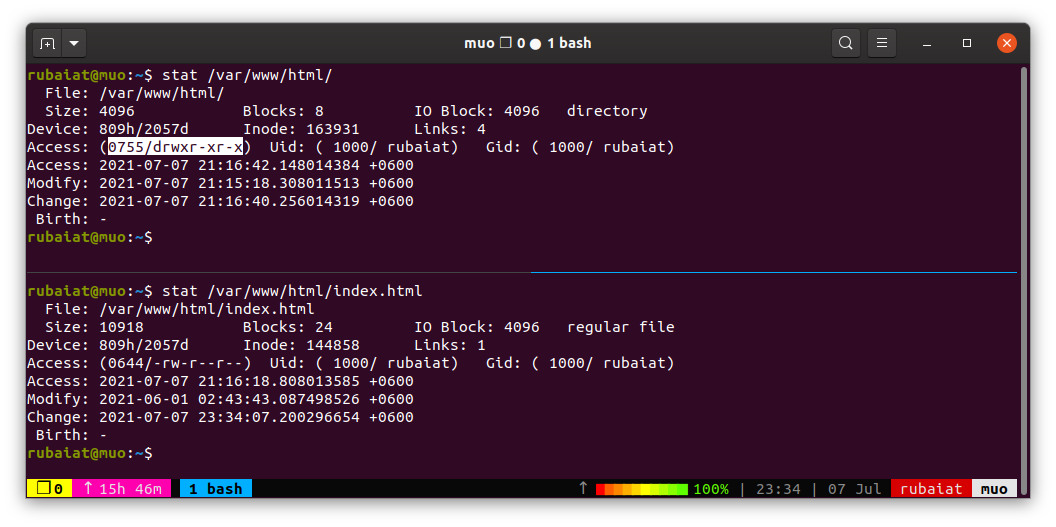
To solve this error, fix your webroot directory permissions. The below command uses the chmod utility to set the directory permissions to 755.
sudo find /var/www/html -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \;This command assumes you're using the default document root of Apache to hold your website. If you're using a different directory, replace the directory name accordingly. Use the below command to change all file permissions to 644.
sudo find /var/www/html -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;The above command uses the find utility to locate individual files and sets the correct permission via chmod. The ending {} \ holds the file paths returned by the find command, and the semicolon (;) marks the end of the iteration. Finally, restart the Apache server so your changes can take effect.
sudo systemctl restart apache2.serviceThis command restarts the Apache server on Ubuntu. However, many RPM-based distros like RHEL or CentOS install Apache as httpd. For such systems, use the following command instead:
sudo systemctl restart httpd2. Fix the .htaccess File for Your WordPress Website
The .htaccess file serves as a distributed config file and tells Apache how to handle things like configuration changes per directory. Sometimes this file can get corrupted and may result in the "you don't have permission to access on this server" error.
Luckily, if that's what is causing the 403 error on your server, you can easily fix this by creating a new .htaccess file. In order to create a new .htaccess file for your website, first, log in to your WordPress dashboard. Then, click on Settings > Permalinks.
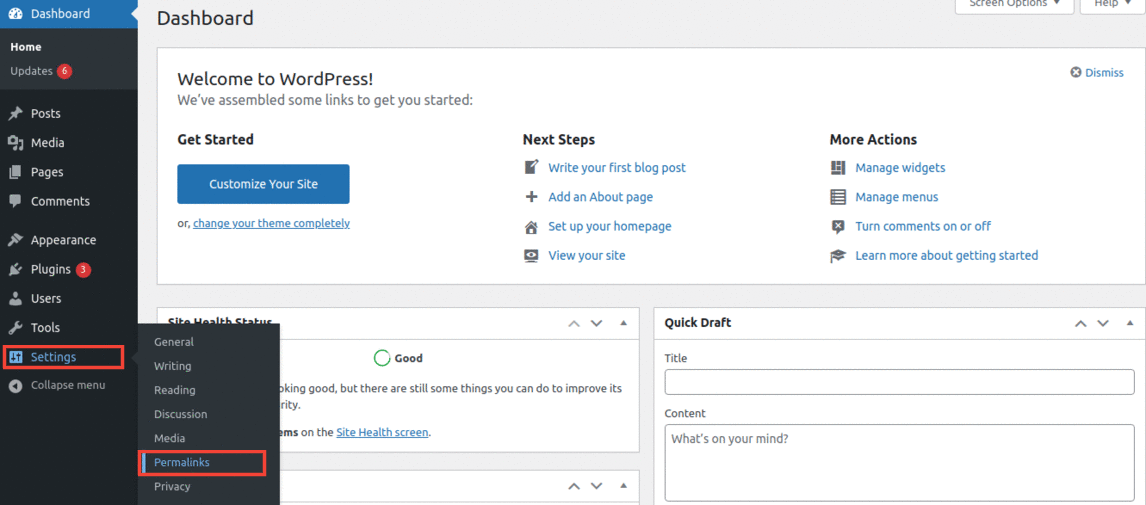
You don't have to make any additional changes here. Just click on the Save Changes button and WordPress will generate a fresh .htaccess file for you.
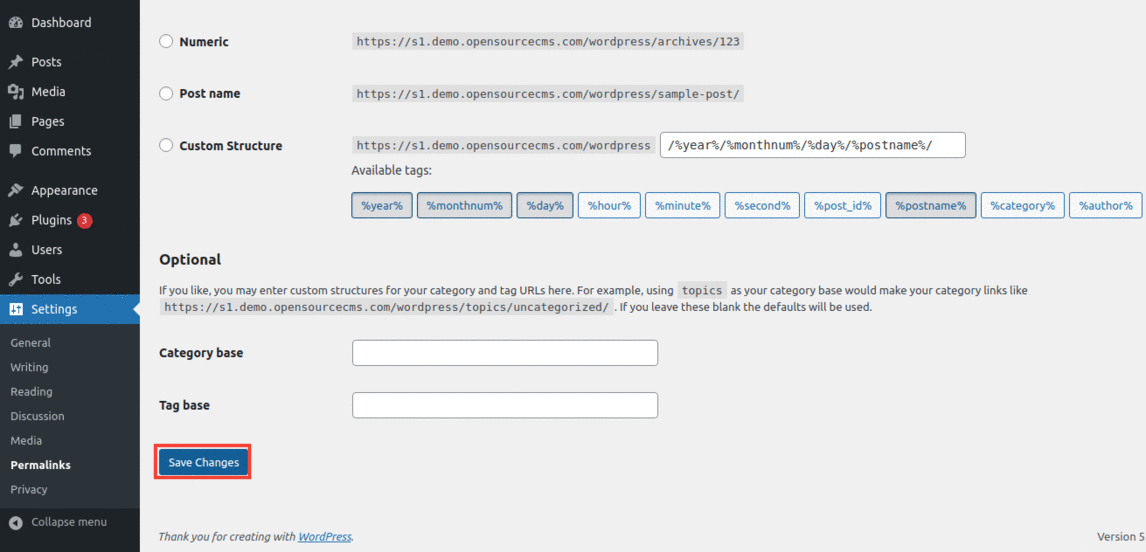
So anytime you face the above problem, try creating a new .htaccess file. The .htaccess method usually works well for WordPress websites.
3. Configure Directives in the Apache Configuration File
Apache 2.4 makes use of a new configuration module named mod_authz_host. This module exposes several new directives. In short, this implements the following rules:
- Require all granted: Allow all requests
- Require all denied: Deny all requests
- Require host safe.com: Only permit requests from safe.com
If you're using Apache 2.4, make sure your main configuration file contains the following block of code. You can check out the contents of this file using a simple text editor like Vim. Add this block in the configuration file if they're missing. Then, you can save and exit Vim.
vim /etc/apache2/apache2.conf<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all denied
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share>
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>Moreover, if you're running an RHEL-based web server, you need to ease access to the /var/www section in your Apache configuration file. So make sure the /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf file contains the following block of code.
vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf<Directory "/var/www">
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>Finally, restart the Apache server using one of the following commands.
# for Ubuntu and Debian
sudo systemctl restart apache2.service# for RHEL and CentOS
sudo systemctl restart httpdFix the Apache Server Permission Error
A lot of people face the above issue when accessing public websites or configuring their own sites. This guide covered several fixes to this problem. Resetting the filesystem permission for Apache should be the first resort. If the error persists even after changing the permissions, try creating a new .htaccess file and ensure directives are set properly in your Apache configuration file.
There are many more issues that can result in a server-side error similar to this one. You need to be proficient at troubleshooting Linux server issues to get your server up and running in such situations.
0 Comments