Unlike Windows, macOS, and Android, software on Ubuntu—and Linux in general—is not distributed as a single package. Instead, when you install an application, your system's package manager downloads multiple packages, including the main app package and its dependencies. However, this only stands true for traditional package installation on Linux i.e. using package managers.
Knowing what additional dependencies are downloaded during an installation can be beneficial for beginner and advanced users alike. This way, one has complete control over the packages installed on their system.
Let's take a look at how you can check the dependencies of a package on Ubuntu.
What Are Package Dependencies?
Dependencies are supporting packages required for the proper working of an application in Linux. For example, if you want to download the VLC media player on Ubuntu, APT will install some additional packages like libc6 and gcc, in addition to the primary "vlc" package. A dependency can also have other packages as its dependencies, therefore, forming a hierarchical structure.
Since Linux packages are interdependent, almost every software requires additional packages that you have to install on your system.
Although package managers like APT automate the management and installation of said dependencies, errors do occur when you try to build the package manually from the source. However, you can solve such errors by simply installing the required dependency on your system using the apt install command.
How to Check Package Dependencies in Linux
Luckily, on Ubuntu, there are several ways to get a list of dependencies of a package. APT, the default package manager in Ubuntu and Debian-based distros, offers multiple commands to get dependency-related information of a package.
Using the APT Package Manager
You can use APT in Ubuntu to get a list of dependencies associated with a package. The basic syntax of the command is:
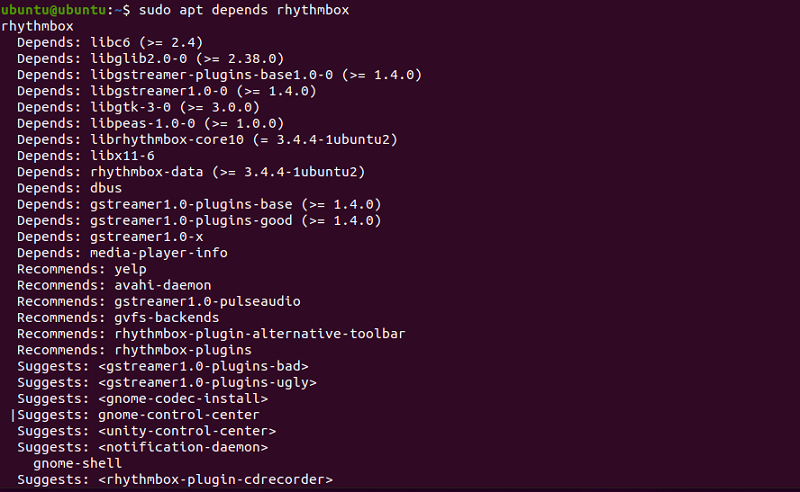
sudo apt depends packagenameFor example, to check dependencies for the rhythmbox package:
sudo apt depends rhythmboxApart from the list of dependencies, the output will also include recommended and suggested packages that you can install alongside rhythmbox.
Alternatively, you can also use the apt-cache command to get the same output.
sudo apt-cache depends rhythmboxTo get additional information related to a specific package, use the show method instead of depends.
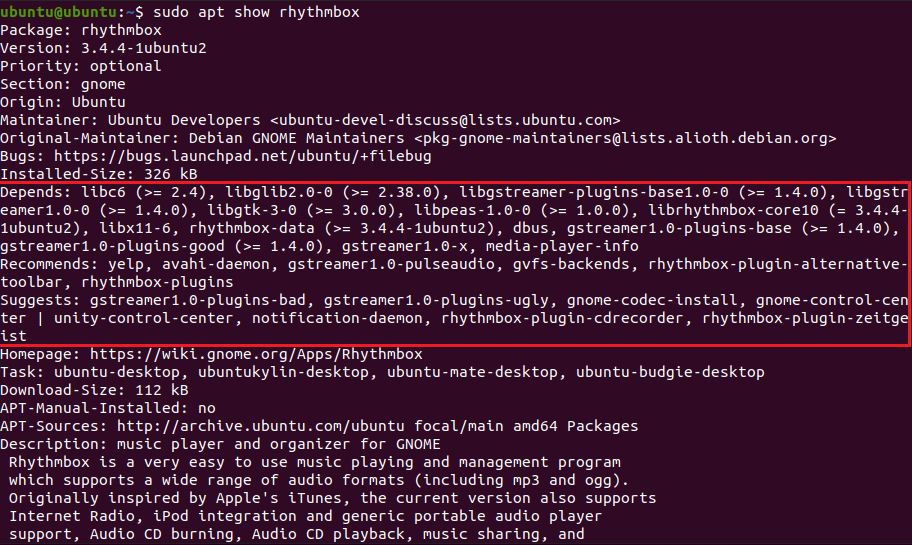
sudo apt show rhythmbox
sudo apt-cache show rhythmboxOutput:
Listing Dependencies Using dpkg
If you have downloaded a DEB package on your system and want to know which dependencies will be installed along with the package, you can use the -I (capitalized i, not lowercase L) or --info flag with the command.
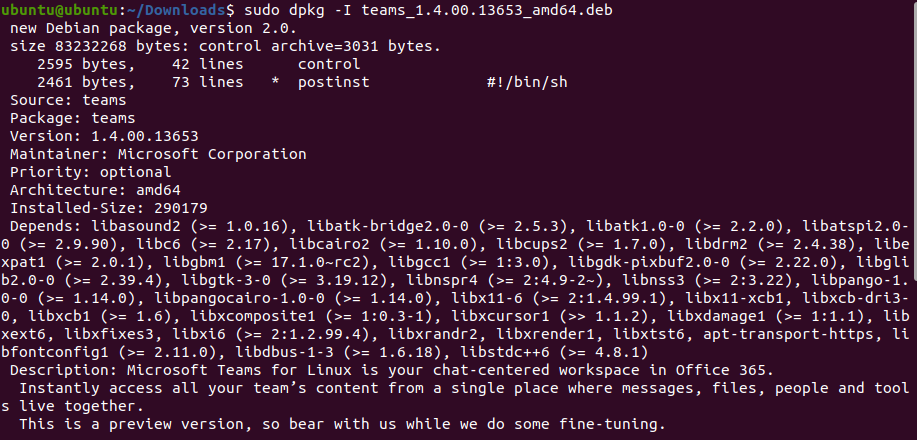
sudo dpkg -I /path/to/package.deb
sudo dpkg --info /path/to/package.deb...where /path/to/package.deb is the absolute or relative path to the DEB file.
The output will display the size of the package, the source, and other useful information along with the list of dependencies.
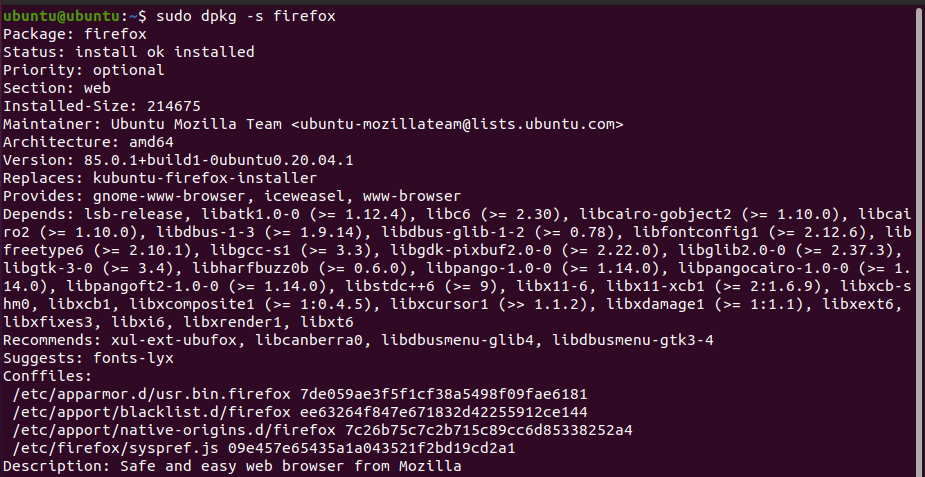
To get the list of dependencies for an installed package, use the -s flag with dpkg. For example:
sudo dpkg -s firefoxOutput:
Using apt-rdepends
To get a more detailed output, you can use the apt-rdepends utility. Since it doesn't come preinstalled on most Linux distributions, you will have to install it manually on Ubuntu using APT.
sudo apt install apt-rdependsUse the following command format to get the dependency tree for a package:
apt-rdepends packagenameFor example:
apt-rdepends vlcOutput:
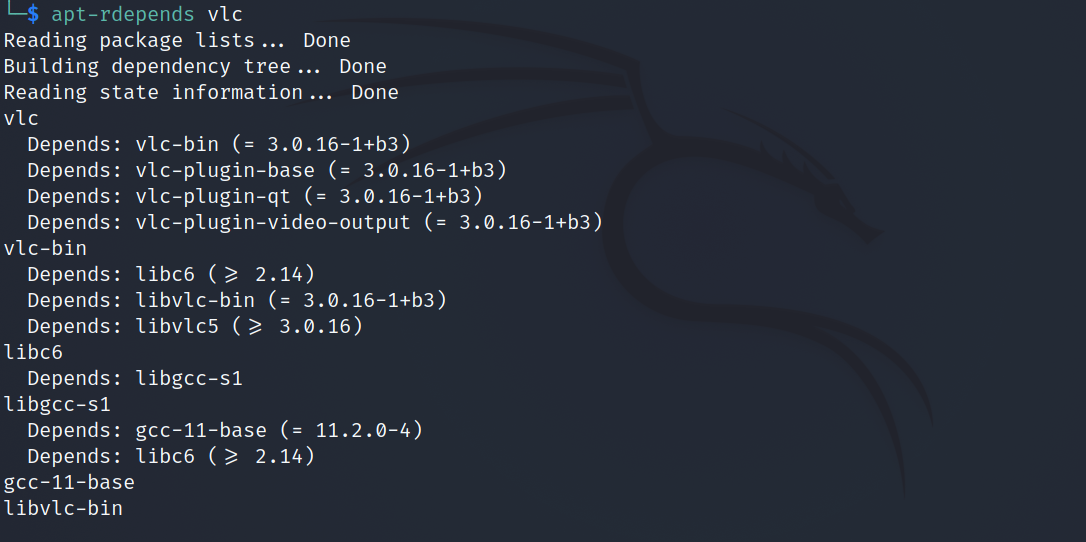
The output generated is generally long as apt-rdepends displays a complete hierarchical tree of dependencies, which means you also get the list of dependencies of a dependency.
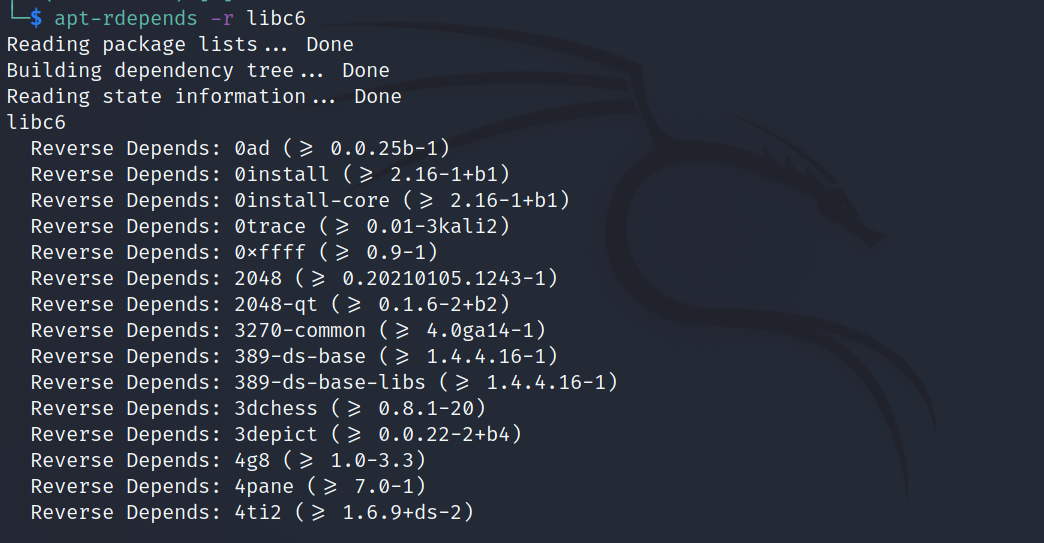
You can also get a list of packages that depend on a particular package. For example, to check which packages require libc as a dependency:
apt-rdepends -r libcOutput:
The reverse-depends Utility
Although the reverse dependency feature (the -r flag) of apt-rdepends works better than expected, there's yet another utility you can use to extract reverse dependencies of a package. The reverse-depends command is a part of the ubuntu-dev-tools package, and can be downloaded using:
sudo apt install ubuntu-dev-toolsThe default syntax of the command is:
reverse-depends options packagename...where options are the flags you can use with the command and packagename is the name of the package you want to reverse check the dependencies for.
You can also add various flags to the aforementioned command to modify the output. Here's a list of the most useful options:
- -R: List only direct dependencies (no suggested or recommended packages)
- -s: Include suggested packages
- -l: Present the output in a cleaner format, appropriate for usage in scripts
In case you can't figure out how to use the tool and need command-line help, use the --help or -h flag.
reverse-depends -h
reverse-depends --helpGet Dependency List Using a Simulated Installation/Removal
For those who want a brief list of all the dependencies that are currently not installed on the system, you can run a simulated installation (or uninstallation) of a particular package.
To check the dependencies required by the PHP package, for example, run the following command:
sudo apt install -s phpThe output will contain a "The following additional packages will be installed" section. All the package names listed further are dependencies that were not found on your system.
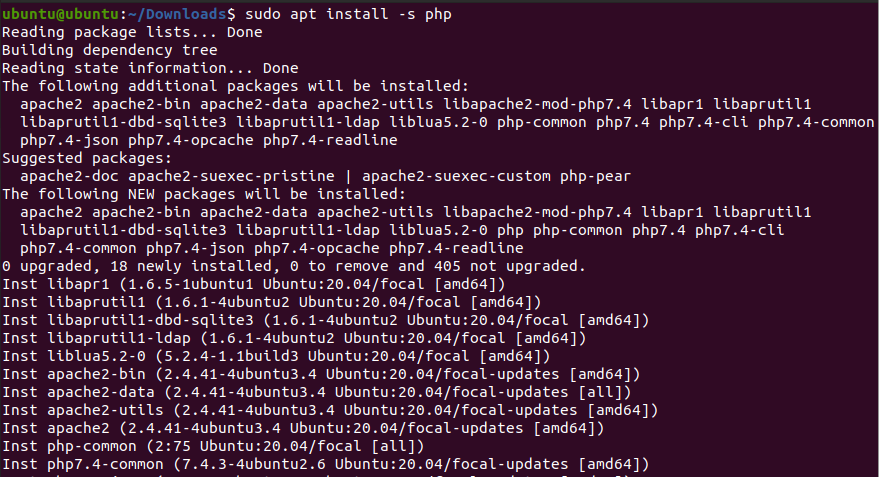
If you want to get a list of dependencies for a package already installed on Ubuntu, you can perform a simulated uninstall to check which additional packages will be removed with it.
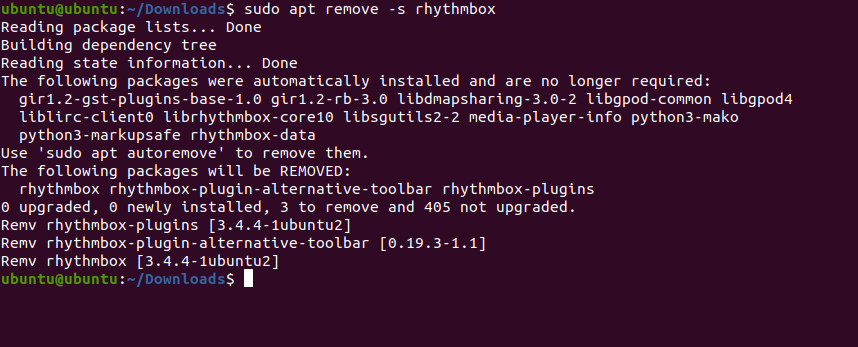
sudo apt remove -s packagenameExample:
sudo apt remove -s rhythmboxOutput:
Linux Packages Are Interdependent
As you can fairly deduce from this guide, almost every Linux package depends on another package. The primary principle behind this concept is that on Linux-based operating systems, each package is supposed to do a single job, and do it well.
If a package has been developed for managing audio services, then other programs will simply list the said package as their dependency, and use it to fulfill their audio requirements.
Also, in case multiple applications demand the same package, it is only installed once on the system, preventing data redundancy and saving storage space on the disk. You can also get a list of all the currently installed packages on your system using APT.
0 Comments